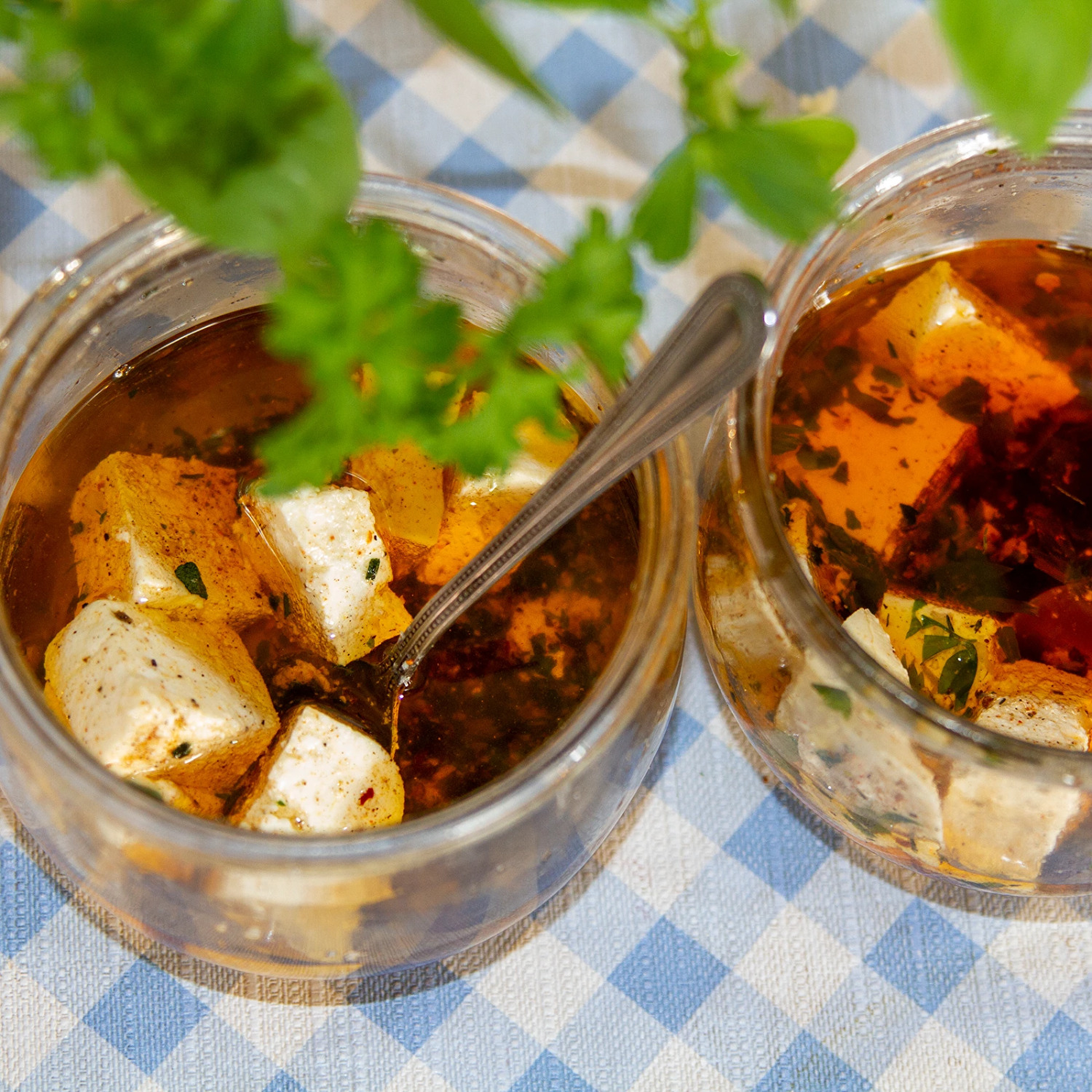
The BROWIN 411241 Bacterial Cultures for Greek Cheese are a perfectly selected mix of lyophilized lactic acid fermentation bacteria, enabling you to prepare delicious feta-type Greek cheese. This mix is an excellent foundation for a healthy diet and is also gluten-free.
- Ideal for home production of feta-type Greek cheese: The addition of these bacteria speeds up and stabilizes the entire process.
- Easy to use: Utilizing the mixture of lyophilized meso- and thermophilic lactic fermentation bacteria in home cheese production does not require specialized knowledge or skills.
- Long shelf life: Being lyophilized, these bacteria are dried at low temperatures under high pressure, allowing for long-term storage without loss of effectiveness.
- Extremely efficient: This mixture can ferment up to 40 liters of milk.
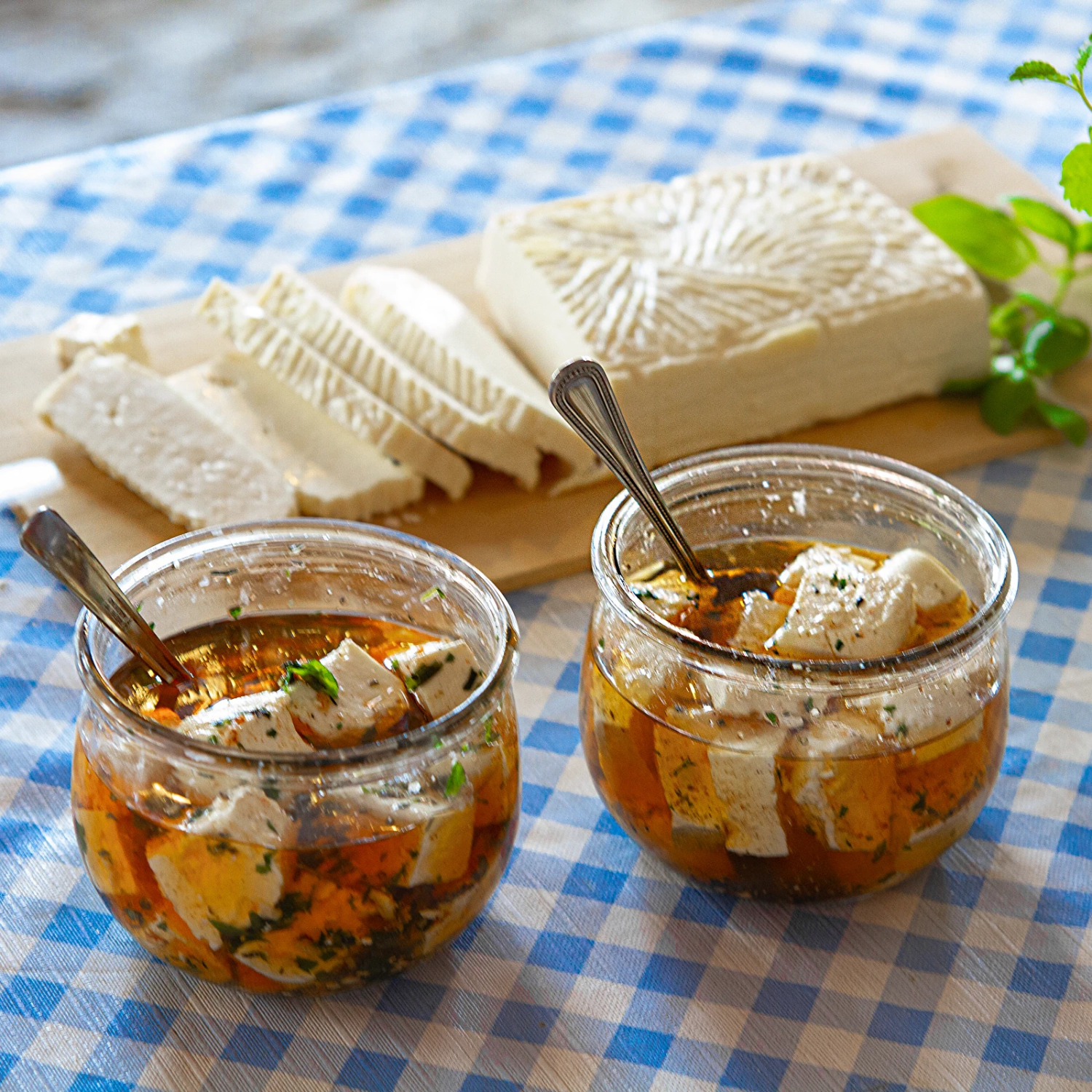
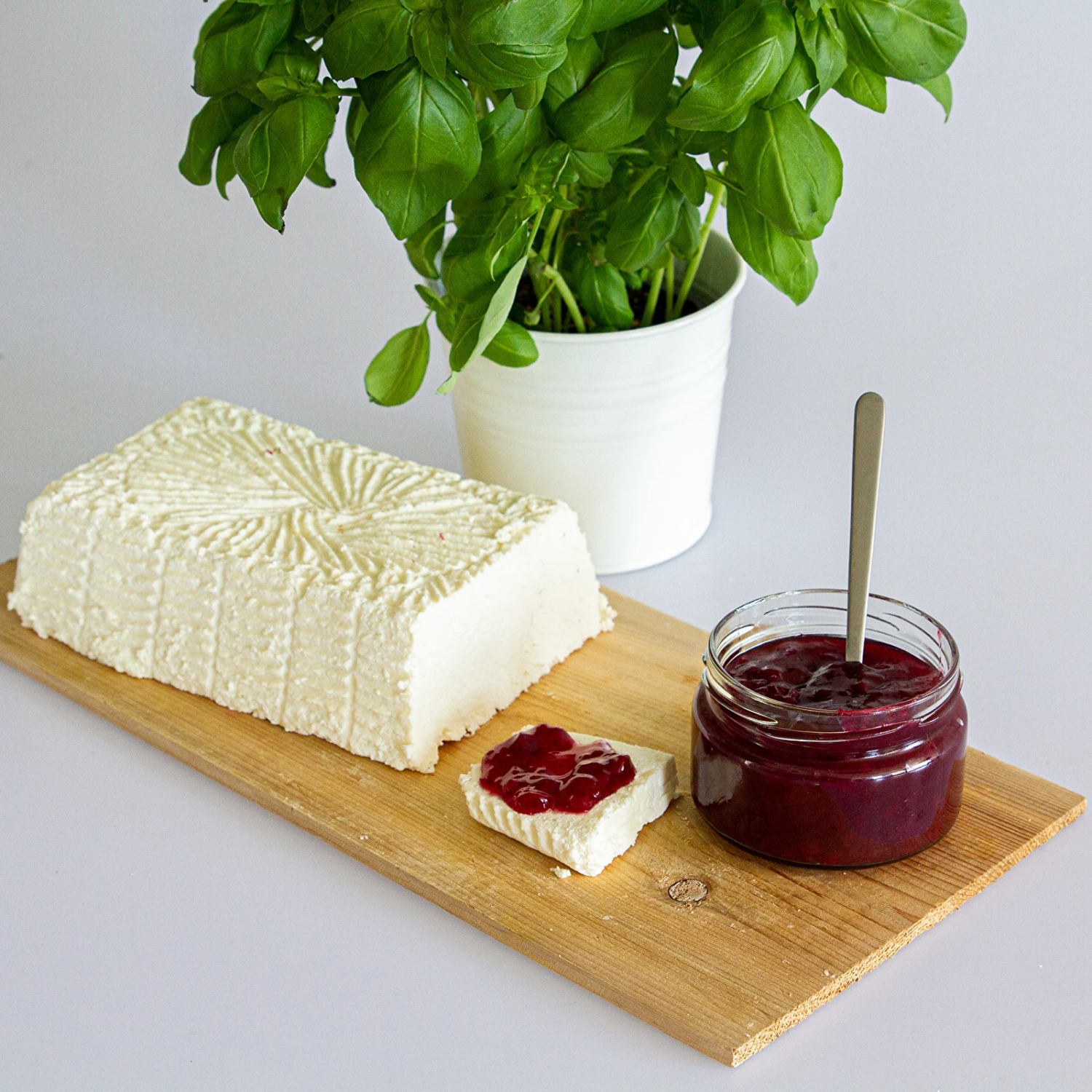
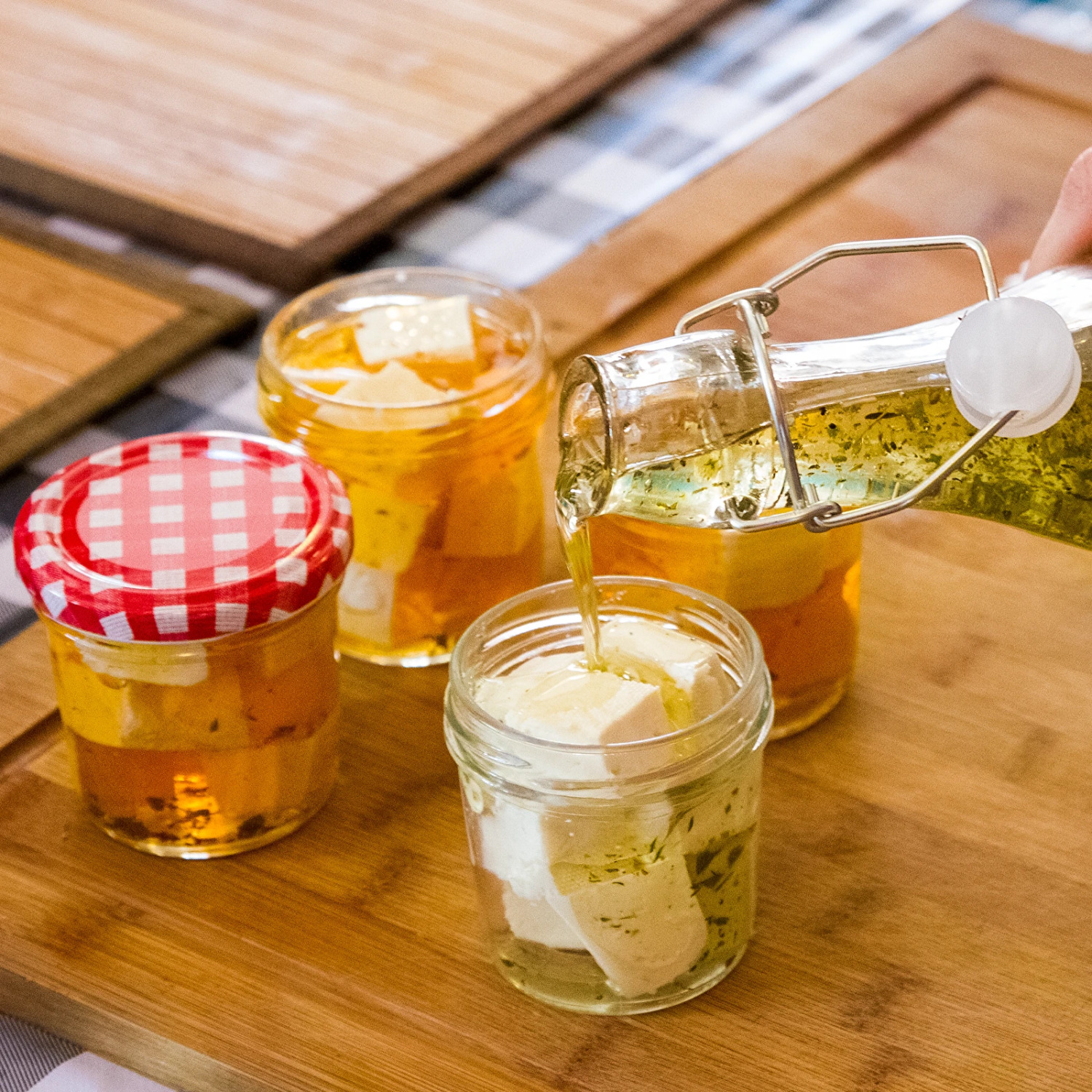
- Versatile enjoyment: The cheese can be eaten raw or used as an ingredient in salads, starters, and various main dishes. Visit our Recipe Book for more inspiration.
This blend of lyophilized meso- and thermophilic lactic acid fermentation bacteria is the perfect starter and additive for producing homemade feta cheese. Thanks to this carefully selected bacteria mix, the fermentation process is quicker and more stable, resulting in cheese with a uniform texture and flavor.
How to use:
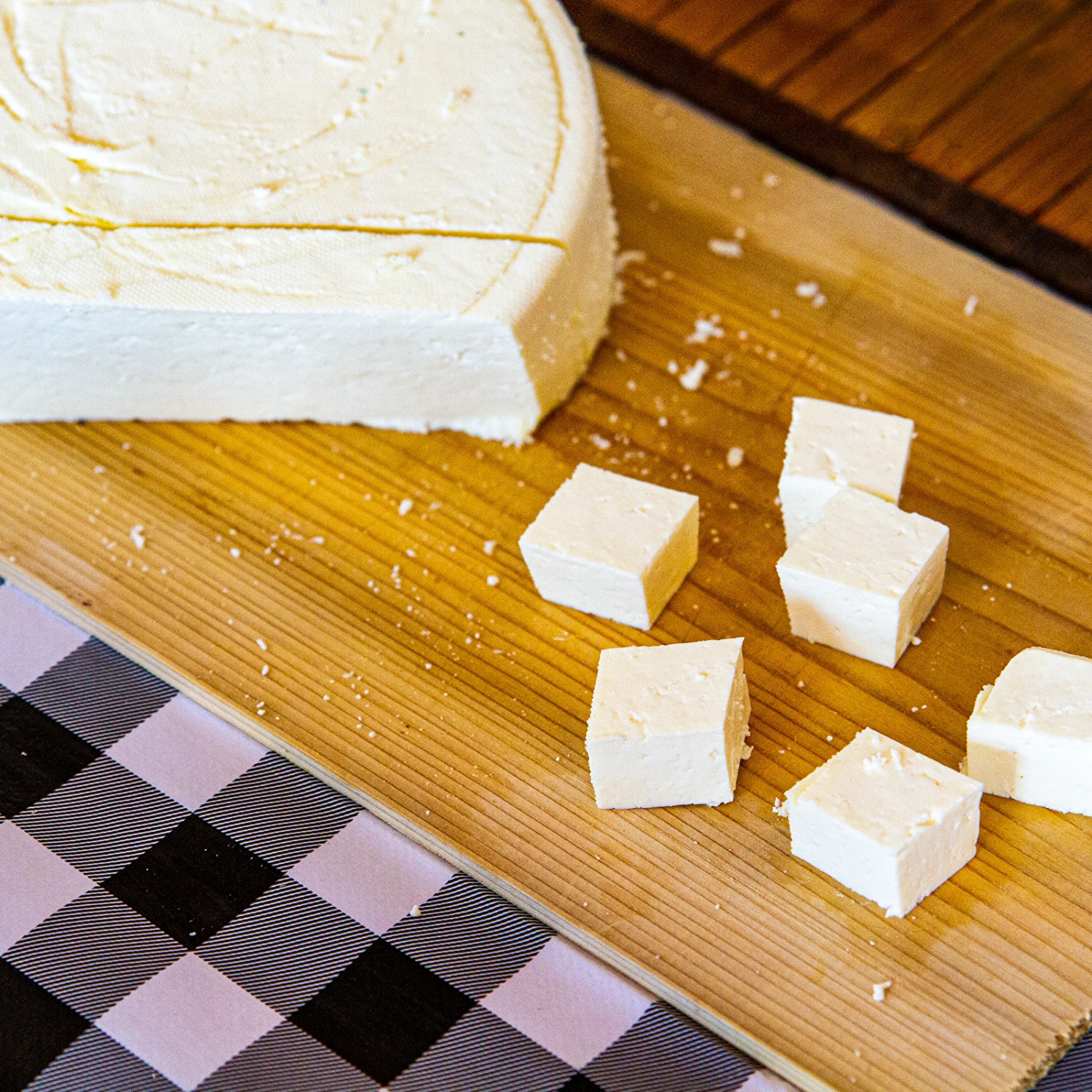
If using fresh milk straight from the cow, pasteurization is recommended at about 65°C for 30 minutes. Pour 6 liters of milk into a pot and heat it to 33°C. Turn off the heat. Dissolve approximately 0.4 g of bacteria in a small amount of lukewarm water and add it to the milk, mixing thoroughly. Cover the container and let it sit for about 1 hour. If you used store-bought milk pasteurized at a low temperature, add about 1 g of bulk calcium chloride. If you're using fresh milk, the addition of calcium chloride is unnecessary. Heat the milk to 38°C, then add about 0.6 g of dried rennet, dissolved in a little lukewarm water. Stir the milk briskly. After about 50 minutes, cut the curd into 1-2 cm cubes and let it rest for 10-15 minutes for whey separation. Press the curd with a strainer and remove most of the whey with a ladle. After the whey is mostly separated, transfer the curd to cheesecloth and place it in a cheese press. Gradually increase the pressure. After reaching around 5 kg of pressure, let the cheese rest for at least 12 hours at room temperature. Move the cheese to a brine solution (1 L water + 180 g salt) for 6 hours, followed by another brine (1 L water + 70 g salt) for storage, keeping it in the fridge.
Ingredients: Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactobacillus lactis subsp. cremoris, lactose.
Best before date: It considers the possibility of transporting the product at temperatures below 30°C for up to 7 days.
You can find detailed recipes for different types of cheese in the Cheesemaking Calculator.

Garden equipment
Hand tools
Tools
Abrasives, drills, blades
Construction tools
Autokaubad
Garden tools
Welding equipment
Work clothes and accessories
Lighting and electrictronics
Construction chemicals
Fasteners
Heating and ventilation
Tourism